Answer:
Quotient:
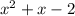
Remainder:
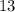
P(-2):
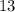
Explanation:
Remember that the remainder theorem states that the remainder when a polynomial p(x) is divided by (x - a) is p(a).
To calculate the quotient, we'll do the synthetic division as following:
Step one:
Write down the first coefficient without changes
Step two:
Multiply the entry in the left part of the table by the last entry in the result row (under the horizontal line).
Add the obtained result to the next coefficient of the dividend, and write down the sum.
Step 3:
Multiply the entry in the left part of the table by the last entry in the result row (under the horizontal line).
Add the obtained result to the next coefficient of the dividend, and write down the sum.
Step 4:
Multiply the entry in the left part of the table by the last entry in the result row (under the horizontal line).
Add the obtained result to the next coefficient of the dividend, and write down the sum.
Now, we will have completed the division and have obtained the following resulting coefficients:
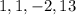
Thus, we can conlcude that the quotient is:
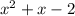
And the remainder is 13, which is indeed P(-2)