First we will calculate the vertical asymptote, is when the denominator of the function given is equal to zero
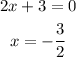
then we will calculate the horizontal asymptote because the degree of the numerator and the denominator is equal we can calculate the horizontal asymptote with the next operation
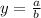
a= the coefficient of the leading term of the numerator
b=the coefficient of the leading term of the denomintor
in our case
a=4
b=2
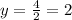
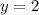
As we can see the graph that shown the asymptotes of the function is the graph in the option C.