When b²−4ac=0 there is one real root.
When b²−4ac>0 there are two real roots.
When b²−4ac<0 no real roots or two complex roots
First equation
-x²-4x+7
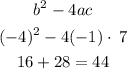
b²−4ac>0, then equation -x²-4x+7 has two real roots.
Second equation
-2x²+9x-11
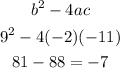
b²−4ac<0, then equation -2x²+9x-11 has two complex roots.
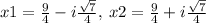
Third equation
3x²-6x+3
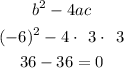
b²−4ac=0, then equation 3x²-6x+3 has one root.