Answer:
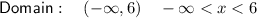
![\textsf{Range}: \quad (-\infty,6] \quad -\infty < y\leq 6](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/4oaszousv0mqty1os4o6280snct8vcz15y.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values).
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (y-values).
An open circle indicates the value is not included in the interval.
A closed circle indicates the value is included in the interval.
An arrow show that the function continues indefinitely in that direction.
Interval notation
- ( or ) : Use parentheses to indicate that the endpoint is excluded.
- [ or ] : Use square brackets to indicate that the endpoint is included.
Inequality notation
- < means "less than".
- > means "more than".
- ≤ means "less than or equal to".
- ≥ means "more than or equal to".
From inspection of the given graph, the function is not continuous and so the domain is restricted.
There is an open circle at x = 6.
Therefore, the domain of the function is:
- Interval notation: (-∞, 6)
- Inequality notation: -∞ < x < 6
From inspection of the given graph, the maximum value of y is 6.
The function continues indefinitely to negative infinity.
Therefore, the range of the function is:
- Interval notation: (-∞, 6]
- Inequality notation: -∞ < y ≤ 6