When looking at a graph of a line, there are two things you should look for straight off the bat. First, the y-intercept. And second, the slope.
The equation of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope, b is the y-intercept, and x is the input.
What is slope?
Slope is a number that determines how the line changes. It is often referred to as the "rate of change" because it represents how much the y-value of the line changes when the input (x) changes. The formula for slope is:
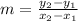
Breakdown: This formula represents the change in the line, typically left to right. It shows the change in x-value over the change in corresponding y-value. This is also known as "rise over run," because the y-value is how much the line changes vertically, while the x-value is how much it changes horizontally.
Example: Let's say our line has a slope of 4, or m = 4/1. This means the y-value will change 4 units when the x-value changes by 1.
What is y-intercept?
Y-intercept is a value that determines the location of the line. When x = 0, the value of b will be the y-value. Essentially, when the line crosses the y-axis, that will be the y-value of the line.