Answer:
See below for all the cube roots
Explanation:
DeMoivre's Theorem
Let
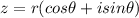 be a complex number in polar form, where
be a complex number in polar form, where
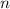 is an integer and
is an integer and
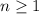 . If
. If
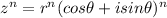 , then
, then
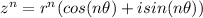 .
.
Nth Root of a Complex Number
If
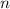 is any positive integer, the nth roots of
is any positive integer, the nth roots of
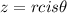 are given by
are given by
![\sqrt[n]{rcis\theta}=(rcis\theta)^{(1)/(n)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/obtv0iu9kenxdiqblofcqhv1ja8cn4baw2.png) where the nth roots are found with the formulas:
where the nth roots are found with the formulas:
![\sqrt[n]{r}\biggr[cis((\theta+360^\circ k)/(n))\biggr]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8wjm839b4f4ch0qeok2niofktvtai50e2q.png) for degrees (the one applicable to this problem)
for degrees (the one applicable to this problem)
![\sqrt[n]{r}\biggr[cis((\theta+2\pi k)/(n))\biggr]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/1iqjwzt8qpj6hlqzej0q1qmj4mswu2b2uz.png) for radians
for radians
for
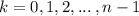
Calculation
![z=27(cos330^\circ+isin330^\circ)\\\\\sqrt[3]{z} =\sqrt[3]{27(cos330^\circ+isin330^\circ)}\\\\z^{(1)/(3)} =(27(cos330^\circ+isin330^\circ))^{(1)/(3)}\\\\z^{(1)/(3)} =27^{(1)/(3)}(cos((1)/(3)\cdot330^\circ)+isin((1)/(3)\cdot330^\circ))\\\\z^{(1)/(3)} =3(cos110^\circ+isin110^\circ)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/eswceykxe9pjf4554162tndq1ex7l6kf51.png)
First cube root where k=2
![\sqrt[3]{27}\biggr[cis((330^\circ+360^\circ(2))/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis((330^\circ+720^\circ)/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis((1050^\circ)/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis(350^\circ)\biggr]\\3\biggr[cos(350^\circ)+isin(350^\circ)\biggr]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/pp1eu9i31i2dym0fzdephit5wvlt8cmap0.png)
Second cube root where k=1
![\sqrt[3]{27}\biggr[cis((330^\circ+360^\circ(1))/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis((330^\circ+360^\circ)/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis((690^\circ)/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis(230^\circ)\biggr]\\3\biggr[cos(230^\circ)+isin(230^\circ)\biggr]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mc5e2z1doi9xjabrbr9lc3kqzz2m7b3hqk.png)
Third cube root where k=0
![\sqrt[3]{27}\biggr[cis((330^\circ+360^\circ(0))/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis((330^\circ)/(3))\biggr]\\3\biggr[cis(110^\circ)\biggr]\\3\biggr[cos(110^\circ)+isin(110^\circ)\biggr]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yii3nc9kza5t81dyg0rki1rxygbc9yv6vi.png)