We have a terminal point (-3,-5).
We have to find cos(θ), csc (θ and tan)(θ.)
We can locate the terminal point and the angle as:
The cosine of this angle will be negative, as ( is located in the third quadrant)
The hypotenuse of this right triangle will be called R and we can calculate it using the Pythagorean theorem:
![\begin{gathered} R^2=x^2+y^2 \\ R=\sqrt[]{x^2+y^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/oajv3zq3bx1lwutv3vrk0yelg7bvuq8hvl.png)
We can estimate the cosine as:
![\begin{gathered} \cos (\theta)=(x)/(R) \\ \cos (\theta)=\frac{-3}{\sqrt[]{(-3)^2+(-5)^2}} \\ \cos (\theta)=\frac{-3}{\sqrt[]{9+25}} \\ \cos (\theta)=\frac{-3}{\sqrt[]{34}} \\ \cos (\theta)=\frac{-3\sqrt[]{34}}{34} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/v55g7lw6xmm2nvsp44rzn9ikl6n6kqp0p3.png)
We can now relate this to the csc(θ) as:
![\begin{gathered} \csc (\theta)=(1)/(\sin (\theta)) \\ \csc (\theta)=(1)/((y)/(R)) \\ \csc (\theta)=(R)/(y) \\ \csc (\theta)=\frac{\sqrt[]{34}}{-5} \\ \csc (\theta)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{34}}{5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/sy8lfcohfbzss5y8qqo29pp1wl9etuopye.png)
Finally, we can calculate the tangent as:
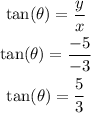
Answer:
cos(θ) = -3√34/34
csc(θ) = -√34/5
tan(θ) = 5/3