Given:
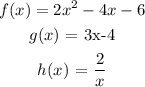
1.1.1 The equation of the reflection of g(x) in the x-axis is of the form:
The rule for the reflection in the x-axis:
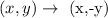
Applying the rule:
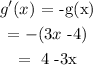
Hence, g'(x) = 4-3x
1.1.2 The equation of the reflection of h(x) in the y-axis.
The rule for reflection in the y-axis:
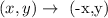
Applying the rule:
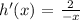
Hence, h('x) = 2/-x
1.1.3 The values of k for which :
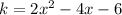
Re-arranging:
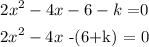
Using the rule that for an equation to have non-real roots, the discriminant (D) must be less than zero.
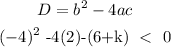
Simplifying we have:
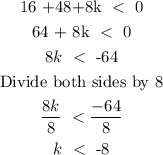
Hence, the values of k for which the equation has non-real roots is that k must be less than -8
1.1.4 The average gradient of f(x) between x=-4 and x=0:
First, we need to find the value of f(x) at x=-4.
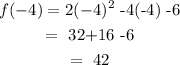
Next, we must find the value of f(x) at x=0:
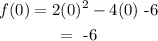
Using the average gradient formula:
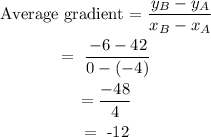
Hence, the average gradient is -12