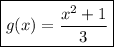Answer:
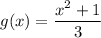
Explanation:
Given functions:
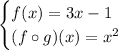
Composite functions are when the output of one function is used as the input of another.
Therefore, the given composite function (f o g)(x) means to substitute function g(x) in place of the x in function f(x).
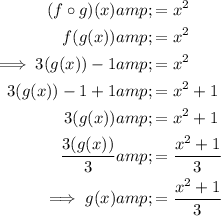
Therefore: