Answer:
One of the first things we need to know is the mass of the astronaut and equipment combined. Weight is given by the formula:
W = m x g, where m is the mass of the object(kg) and g is the gravitational acceleration on Earth's surface(9.8 m/s^2)
Knowing the weight of the astronaut and equipment, we get:
m = W / g
m = 2,156 N / 9.8 m/s^2 ( ^2 represents the power of 2)
m = 219.9 kg
Now, one last thing we need to know is the resulting velocity of the astronaut in the opposite direction. Once the astronaut throws the wrench from their equipment, according to the 3rd law of motion, the astronaut and the wrench will move in opposite directions because the astronaut pushed the wrench, and in return, the astronaut is pushed by the wrench. Having all these, we need to work with momentum.
p = m * v, where p is the object's momentum, m is mass and v is its velocity
let's call
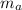 the astronaut's mass(combined with their equipment, including the wrench since it's initially part of the equipment)
the astronaut's mass(combined with their equipment, including the wrench since it's initially part of the equipment)
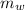 = 5.0 kg is the wrench's mass
= 5.0 kg is the wrench's mass
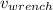 = 5.0 m/s is the wrench velocity after it was thrown
= 5.0 m/s is the wrench velocity after it was thrown
The astronaut's momentum(before the thrown wrench):
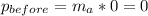 , because the astronaut's initial velocity is zero(including the equipment and wrench)
, because the astronaut's initial velocity is zero(including the equipment and wrench)
The astronaut threw the wrench. Therefore, we get the following momentum:
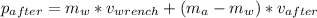
The reason why we subtract the astronaut and equipment mass from the wrench's mass is that the astronaut and the equipment move independently from the wrench, therefore we exclude the wrench's mass.
The 3rd law of motion also implies that the total momentum of a system of objects interacting(colliding against one another) doesn't change. Therefore:
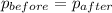
Plugging all the values, we get:
5.0 kg * 5.0 m/s + (219.9 kg - 5.0 kg) *
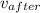 = 0
= 0
Solving the above equation, we get that the resulting velocity of the astronaut in the opposite direction is:
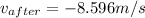
Note: The minus denotes the opposite direction the astronaut has after it was pushed by the wrench.