Answer:
2.85 g
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem, we need to first write out a balanced equation for the reaction:
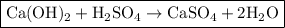
Next, we have to calculate the number of moles of
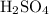 that will be neutralized:
that will be neutralized:
no. of moles of
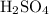 = concentration × volume/1000
= concentration × volume/1000
= 0.850 ×
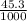
= 0.0385 mol
As we can see from the balanced equation above, the molar ratio of
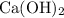 and
and
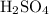 are equal; therefore their mole numbers are also equal.
are equal; therefore their mole numbers are also equal.
This means that 0.0385 moles of
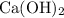 will be required to neutralize the
will be required to neutralize the
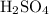 .
.
Now we can calculate the mass of
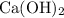 required:
required:
mass = no. of moles × molar mass
= 0.0385 × [40 + 2×(16+1)]
= 0.0385 × 74
= 2.85 g (3 s.f.)
Therefore, 2.85 g of
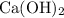 will be needed.
will be needed.