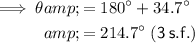Answer:
4. |R| = 60.8 N (3 s.f.)
θ = 34.7° (3 s.f.) relative to the x-axis
5. |F| = 60.8 N (3 s.f.)
θ = 214.7° (3 s.f.) relative to the x-axis
Step-by-step explanation:
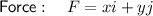
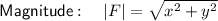
Given:
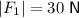
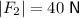
Using the given magnitudes and the force diagram:
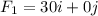
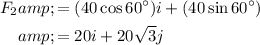
Question 4
The resultant force is the sum of all forces acting on an object.
To find the resultant force, add the corresponding components of the forces:
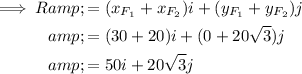
Therefore the magnitude of the resultant force is:
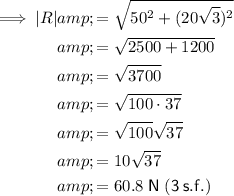
The direction of the resultant force is:
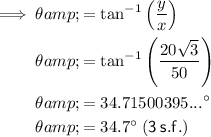
Question 5
An object is in equilibrium if the resultant force on it is zero.
Therefore, the magnitude of the equilibriant force is equal to the magnitude of the resultant force: 60.8 N (3 s.f.).
The direction of the equilibriant force is opposite to the resultant force, so its components will be:
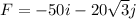
Therefore, it will be in Quadrant III.
So the direction relative to the x-axis will be the same direction as the resultant force plus 180°: