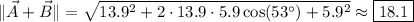Use the dot product identity,
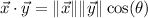
where
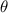 is the measure of the angle between the two vectors
is the measure of the angle between the two vectors
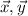 . Note that
. Note that
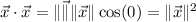
Applying the identity to
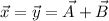 and using the distributive and commutative properties of the dot product, we get
and using the distributive and commutative properties of the dot product, we get
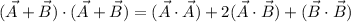
which is equivalent to
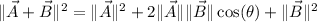
Now, we're given
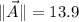 ,
,
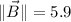 , and
, and
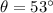 , so that
, so that