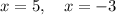Answer:
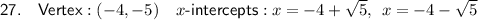
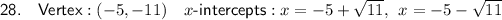

Explanation:
Vertex form of a quadratic function:
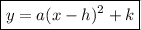
where:
- (h, k) is the vertex.
 is some constant.
is some constant.
Question 27
Given function:
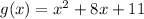
Change to vertex form by completing the square.
Add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x:
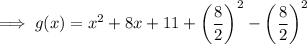
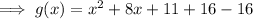
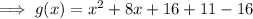
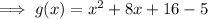
Factor the perfect trinomial:
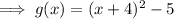
Therefore, the vertex is (-4, -5).
To find the x-intercepts, set the function to zero and solve for x:
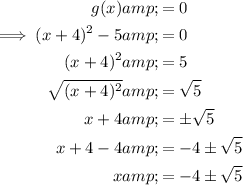
Therefore, the x-intercepts are:
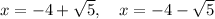
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 28
Given function:
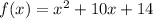
Change to vertex form by completing the square.
Add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x:
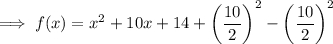
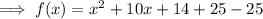
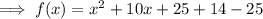
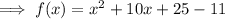
Factor the perfect trinomial:
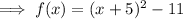
Therefore, the vertex is (-5, -11).
To find the x-intercepts, set the function to zero and solve for x:
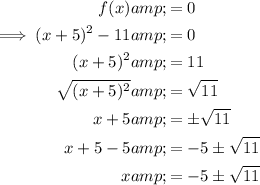
Therefore, the x-intercepts are:
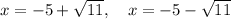
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 29
Given function:
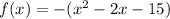
Change to vertex form by completing the square.
Add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x:
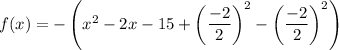
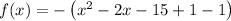
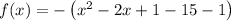
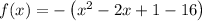
Factor the perfect trinomial:
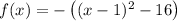
Simplify:
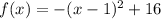
Therefore, the vertex is (1, 16).
To find the x-intercepts, set the function to zero and solve for x:
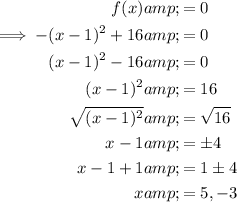
Therefore, the x-intercepts are: