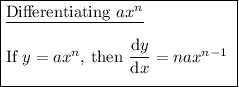Answer:

Explanation:
Given cubic function:
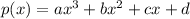
As point (0, 1) is on the curve, substitute x = 0 into the function, set it to 1, and solve for d:
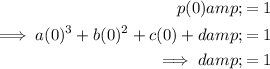
Differentiate the function:
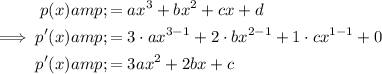
The tangent equation at the point (0, 1) is y = 3x + 1.
Therefore, the gradient of the tangent equation when x = 0 is 3.
To find the gradient of the function at a given point, substitute the x-value of that point into the differentiated function. Therefore, substitute x = 0 into the differentiated function, set it to 3, and solve for c:
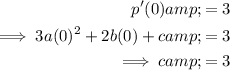
Substitute the found values of c and d into the function:
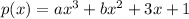
Substitute point (-1, -3) into the function and solve for b:
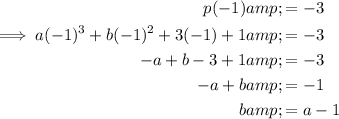
To find the turning points of a function, set the differentiated function to zero and solve for x.
As there is a turning point of function p(x) when x = -1, substitute x = -1 into the differentiated function and set it to zero (remembering to substitute the found value of c = 3 into the differentiated function):
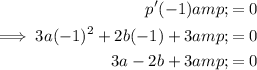
Substitute the found expression for b into the equation and solve for a:
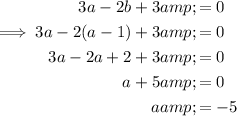
Finally, substitute the found value of a into the found expression for b and solve for b:
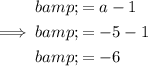
Therefore:
Differentiation Rules