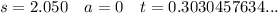Answer:
A) 0.303 s (3 s.f.)
B) 6.76 ms⁻¹ (3 s.f.)
Step-by-step explanation:
Constant Acceleration Equations (SUVAT)
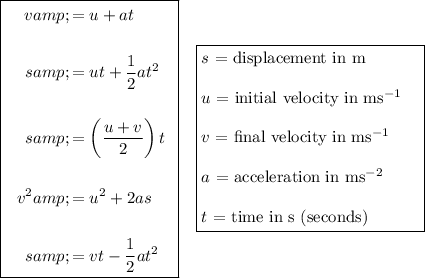
When using SUVAT, assume the object is modeled as a particle and that acceleration is constant.
Consider the horizontal and vertical motion of the projectile separately.
Part A
As the projectile is fired horizontally, the vertical component of its initial velocity is zero.
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 ms⁻²
Resolving vertically, taking ↓ as positive:
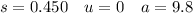

Part B
The horizontal component of velocity is constant, as there is no acceleration horizontally.
Resolving horizontally, taking → as positive: