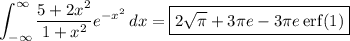Consider the integral
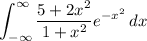
which is the negative of yours. Bit strange to integrate over
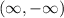 , but if that's what you actually intended, just multiply the final result by -1. Of course, I've already canceled the superfluous factors of
, but if that's what you actually intended, just multiply the final result by -1. Of course, I've already canceled the superfluous factors of
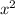 .
.
Expand the integrand into partial fractions.
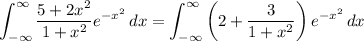
Recall that for
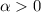 ,
,
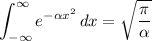
Now let
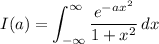
Together, these give
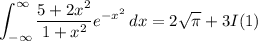
Differentiate
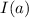 under the integral sign with respect to
under the integral sign with respect to
 to obtain a simple linear differential equation.
to obtain a simple linear differential equation.
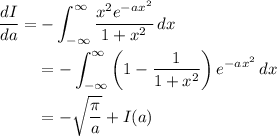
Solve for
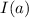 with the initial value
with the initial value
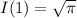 . Using an integrating factor,
. Using an integrating factor,
![\displaystyle (dI)/(da) - I(a) = -√(\frac\pi a) \\\\ e^(-a) (dI)/(da) - e^(-a) I(a) = -√(\frac\pi a)\,e^(-a) \\\\ (d)/(da)\left[e^(-a) I(a)\right] = -√(\frac\pi a)\,e^(-a)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ouocqtzlhwjxnzbo94yo7ijzx2k89bsc27.png)
By the fundamental theorem of calculus,
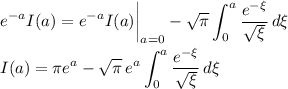
so that
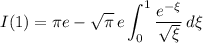
Substitute
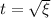 .
.
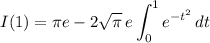
Recall the error function,
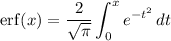
which we can use to write
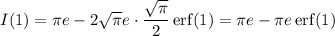
Finally, we arrive at