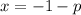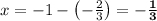Answer:
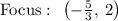
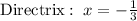
Explanation:
The standard equation for a parabola is
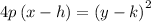
with vertex at (h, k) and a focal length of |p|
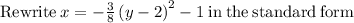 :
:
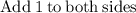
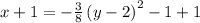 or
or
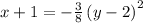
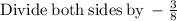
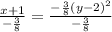
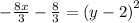
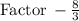
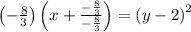
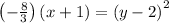
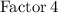
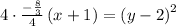
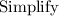
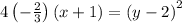
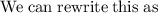
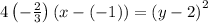
Comparing this with the standard form we get

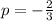
The parabola is symmetric around the x-axis.
The focus lies a distance
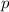 from the center
from the center
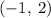 along the x axis
along the x axis
So focus is at
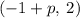
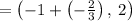
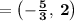
The parabola is symmetric around the x-axis and so the directrix is a line parallel to the y-axis at a distance -p from the center