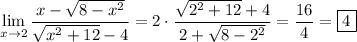The function itself is not well-defined at
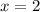 because both numerator and denominator are equal to zero there, so it's discontinuous there. We attempt to remove this discontinuity.
because both numerator and denominator are equal to zero there, so it's discontinuous there. We attempt to remove this discontinuity.
Rationalize the numerator and denominator.
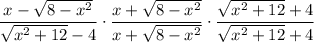
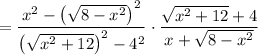
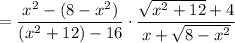
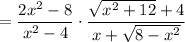
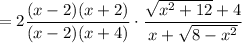
Then in the limit, since
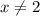 , we can cancel both factors of
, we can cancel both factors of
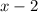 and
and
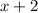 , subsequently removing the discontinuities at
, subsequently removing the discontinuities at
 , and we're left with
, and we're left with
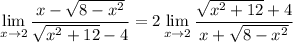
which is now continuous at
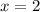 , so we can evaluate directly.
, so we can evaluate directly.