The tetrahedron in question is the set
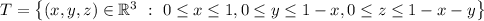
Compute the divergence of the given field.
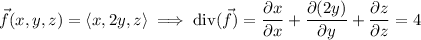
By the divergence theorem, the flux of
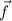 across the boundary of
across the boundary of
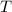 is equal to the integral of the divergence over
is equal to the integral of the divergence over
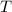 .
.
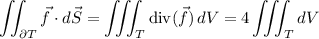
Compute the volume integral. We have
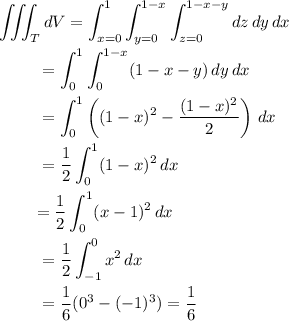
Hence the flux is
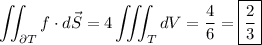
(Thank you stranger for pointing out the error!)