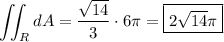I assume you mean the plane
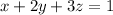 . Its area over the region
. Its area over the region
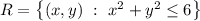
is given by the integral
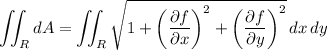
where
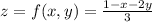 .
.
We have
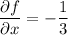
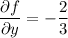
so that the area element is
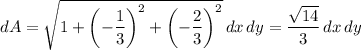
Then we have
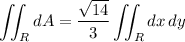
and the remaining integral is exactly the area of the disk
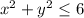 . Its radius is √6, so its area is π (√6)² = 6π. So the area of the surface is
. Its radius is √6, so its area is π (√6)² = 6π. So the area of the surface is