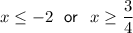Answer:
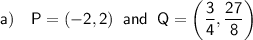
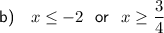
Explanation:
Part (a)
Given equations:
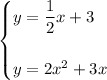
Points P and Q are the points of intersection of the given equations.
Therefore, to find the points of intersection, equate the equations and solve for x:
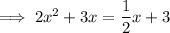
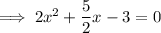
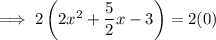
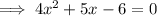
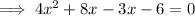
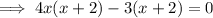
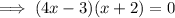
Apply the zero-product property:
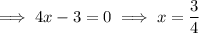
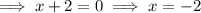
Substitute the found values of x into one of the equations to find the y-coordinates of points P and Q:
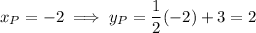
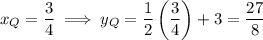
Therefore, the coordinates of P and Q are:
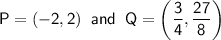
Part (b)
Given inequality:
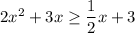
The range of values that satisfies the given inequality is the range of x-values where the curve is equal to or higher than the line.
The curve is equal to or higher than the line for x-values equal to or less than point P and x-values equal to or more than point Q: