(a) If
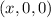 lies on both planes, then
lies on both planes, then
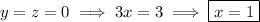
and at the same time

(b) A plane with normal vector
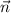 containing the point
containing the point
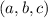 can be written in the form
can be written in the form
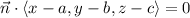
Expanding the left side, we see that the components of
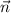 correspond to the coefficients of
correspond to the coefficients of
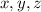 . So the normal vector to
. So the normal vector to
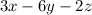 is
is
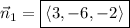 .
.
(c) Similarly, the normal to
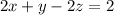 is
is
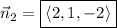 .
.
(d) The cross product of any two vectors
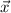 and
and
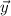 is perpendicular to both of the vectors. So we have
is perpendicular to both of the vectors. So we have
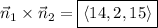
(e) Solve the two plane equations for
 .
.
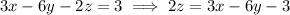

By substitution,
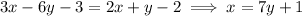
Let
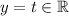 . Then
. Then
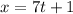 and
and
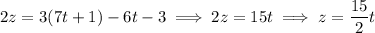
Then the intersection can be parameterized by equations
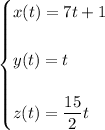
for
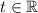 .
.
We can also set
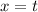 or
or
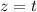 first, then solve for the other variables in terms of the parameter
first, then solve for the other variables in terms of the parameter
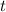 , so this is by no means a unique parameterization.
, so this is by no means a unique parameterization.