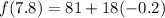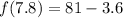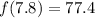Answer:
A
Explanation:
Linear approximation is basically using the equation of a tangent line to approximate values of f.
For example
we have function
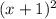
First, things first, let take the derivative to get the gradient function.
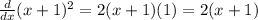
Note: I used the chain rule.
so we get
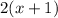
Now, notice the formula for tangent approximation.
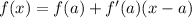
Here x=7.8
a is 8 so we get
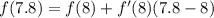
To find f(8), plug 8 into the original function for x.
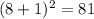
To find f'(8), plug 8 into the derivative function.
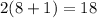
So we get