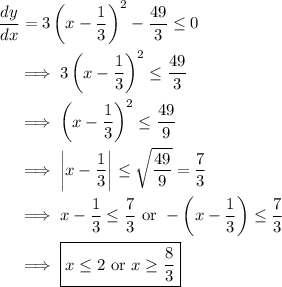9. The curve passes through the point (-1, -3), which means
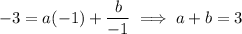
Compute the derivative.

At the given point, the gradient is -7 so that
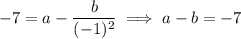
Eliminating
 , we find
, we find
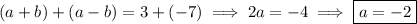
Solve for
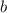 .
.
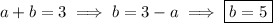
10. Compute the derivative.
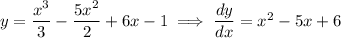
Solve for
 when the gradient is 2.
when the gradient is 2.
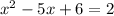
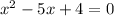
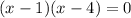
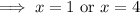
Evaluate
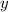 at each of these.
at each of these.
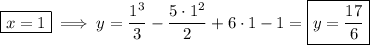
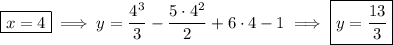
11. a. Solve for
 where both curves meet.
where both curves meet.
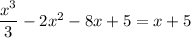
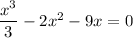
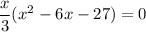
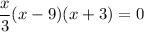
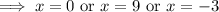
Evaluate
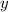 at each of these.
at each of these.
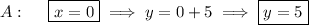
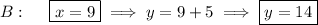
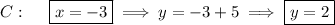
11. b. Compute the derivative for the curve.
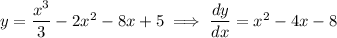
Evaluate the derivative at the
 -coordinates of A, B, and C.
-coordinates of A, B, and C.
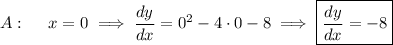
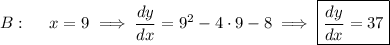
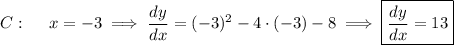
12. a. Compute the derivative.
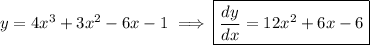
12. b. By completing the square, we have
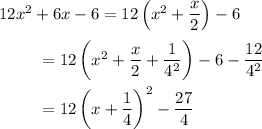
so that
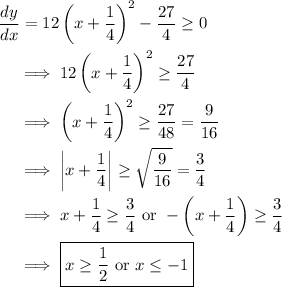
13. a. Compute the derivative.
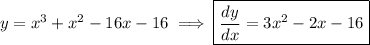
13. b. Complete the square.
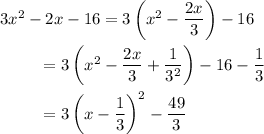
Then