Answer:
2√3
Explanation:
From inspection of the given triangle:
- Side a is opposite angle A ⇒ a = BC
- Side b is opposite angle B ⇒ b = AC
- Side c is opposite angle C ⇒ c = AB
As we cannot be sure that ΔABC is a right triangle since it is not marked as such, use the cosine rule to find the exact length of side a.
Cosine Rule
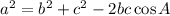
where a, b and c are the sides and A is the angle opposite side a
Given:
Substitute the given values into the formula and solve for a:
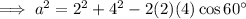
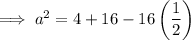
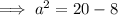
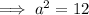
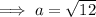
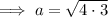
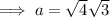
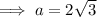
Therefore, the exact length of side a is 2√3.
To find out if ΔABC is a right triangle, use Pythagoras Theorem to solve for side a:
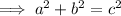
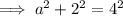
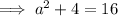
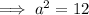
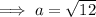
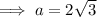
As the measure of side a is the same as the solution found when using the cosine rule, we can conclude that ΔABC is a right triangle.