Answer:
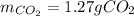
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the combustion of butane is shown below:
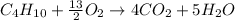
We can evidence the 1:4 and 13/2:4 mole ratio of butane to carbon dioxide and oxygen to carbon dioxide respectively. Thus, in order to compute the maximum amount of carbon dioxide produced in this reaction, we set up the following stoichiometric work:
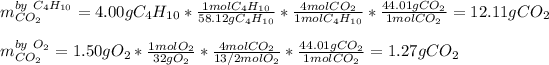
Thus, since oxygen yields the fewest amount of carbon dioxide, we infer the former is the limiting reactant and therefore the maximum amount of carbon dioxide product is 1.27 g.
Best regards!