Answer:
The molar mass of
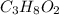 (rounded to three significant figures) is 76.1 amu.
(rounded to three significant figures) is 76.1 amu.
Explanation:
Hey there!
To answer this question, you will need access to a periodic table. You need to know the atomic masses of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) in order to answer this question. With that out of the way, let's begin!
We have a chemical formula:
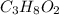 .
.
- The letters are element symbols, which are basically the code for an element. Think of it as an abbreviation or something similar to an ID.
- The subscripts (numbers) help us identify how many atoms of each element are included in the substance.
The first thing we should do is locate C, H, and O on a periodic table and figure out the atomic masses for each element. This will help us determine the total molar mass of the substance.
Determining the Atomic Mass of C
If we locate C on a periodic table, we see that its atomic mass is roughly 12.01 amu (atomic mass units). Then, we have a subscript of 3, so we simply multiply the subscript by the given atomic mass in order to find the atomic mass of the three atoms of carbon.
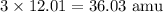
This means that C accounts for 36.03 amu of the molar mass of the substance.
Determining the Atomic Mass of H
Using the same principle as before, we want to find the atomic mass of one atom of H. This is 1.008, so we will multiply 1.008 by the eight atoms (pay attention to the subscript) in order to find the atomic mass of hydrogen in the substance.
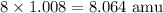
This means that H accounts for 8.064 amu of the molar mass of the substance.
* An important note to add is that we should never round our values until the end of the problem so we make sure to get as close as possible (this is why you learn about accuracy and precision in a chemistry class).
Determining the Atomic Mass of O
Finally, we want to find the atomic mass of O in the substance, so we'll use the same method as before and locate the atomic mass of one atom of oxygen. We find that this is 15.999, which would definitely round to 16.00, but remember the rules for rounding in chemistry in order to be as accurate as possible. Since our subscript is 2, we know that there are two oxygen atoms, so we will multiply the atomic mass of oxygen by 2.
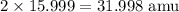
This means that O accounts for 31.998 amu of the molar mass of the substance.
Summation of the Determined Atomic Masses
After you have determined the atomic masses of the atoms in the chemical substance, you have to add these together. This is performed with simple addition.
- C = 36.03 amu
- H = 8.064 amu
- O = 31.998 amu
Now, let's add these together.
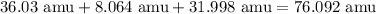
Therefore, the total atomic mass is 76.092 amu.
Rounding to Meet Significant Figures Requirements
Significant figures are used to determine the accuracy of a problem. A basic rule is to use scientific notation to determine how to meet the significant figure request. Since we are rounding to three significant figures, we want to make sure these three figures are significant. There are three basic rules to remember when computing significant figures:
- Any zeroes to the left of the first non-zero number (ex: 0.0981) are insignificant.
- Any zeroes "trapped" in between other non-zero numbers (ex: 9.81075) are significant.
- Any zeroes to the right of the last non-zero number (ex: 5900) are significant ONLY IF they are added after a decimal point and included in the measurement (ex: 5900.)
Therefore, since we need three significant figures, we have to round our value first and then determine the appropriate number of significant figures.
- 76.092 will round to 76.09 first, and then round to 76.1.
- We cannot use 76.09 since there is a trapped zero, which is considered significant.
- We must use 76.1 since there are three significant figures in the value.
Final Answer
Since we have determined that 76.1 fits our requirements for three significant figures, we can safely determine that the molar mass of
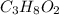 , as determined, is 76.1 amu.
, as determined, is 76.1 amu.