Answer:
Following are the responses to the given question:
Step-by-step explanation:
In point a:
The current ZAR spot ratio by PPP is determined by
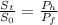 whereas St will be the current level currencies,
whereas St will be the current level currencies,
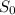 was its base point currency.
was its base point currency.
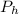 would be in the home nation the market price
would be in the home nation the market price
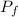 in a different nation was its price standard.
in a different nation was its price standard.
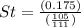
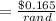
In point b:
According to PPP
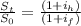
where St= Expected ZAR spot rate in USD with one year
S0= The ZAR spot rate currently exists.
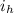 = inflation rate in the home country
= inflation rate in the home country
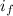 = inflation rate in a foreign country
= inflation rate in a foreign country
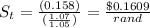
Therefore, it's indeed clear over each year, its dollar was expected to deteriorate relative to a rand as the nation's rising inflation currency is expected to depreciate as per PPP.
In point c:
Under IFE
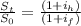
In which St= ZAR spot rate expected with one year in USD
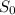 = Current spot rate for ZAR
= Current spot rate for ZAR
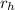 = Homeland interest rate
= Homeland interest rate
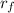 = foreign country interest rate
= foreign country interest rate
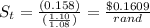
Its dollars also are projected to lose value during the year if the country with such a higher interest will see the currency lose value through IFE.
In point d:
In point (b) and (c), the same is true of PPP, which implies which exchange rates move in the other path of interest rates and an increase in deflation allows prices to rise. If IFE combines both anomalies and leads of a higher percentage nation showing a decline in exchange compared to a lower one. Thus the very same answers would be provided to both PPP and IFE.