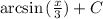Answer:
The result of the integral is:
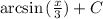
Explanation:
We are given the following integral:
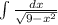
Trigonometric substitution:
We have the term in the following format:
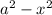 , in which a = 3.
, in which a = 3.
In this case, the substitution is given by:
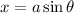
So
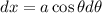
In this question:
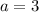
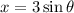
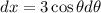
So
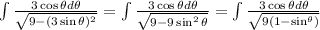
We have the following trigonometric identity:
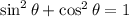
So
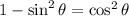
Replacing into the integral:
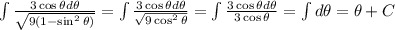
Coming back to x:
We have that:
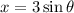
So
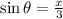
Applying the arcsine(inverse sine) function to both sides, we get that:
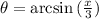
The result of the integral is: