Answer:
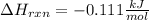
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the total heat flow due to the reaction equals the negative of the calorimeter's heat, we can first compute the former as shown below:
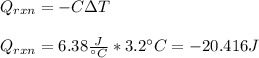
Now, since this total heat flow due to the reaction is defined in terms of the heat of reaction and the total reacted moles:
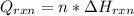
Thus, we compute the moles in 8.5 g of ethanol:
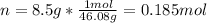
Therefore, the heat of reaction results:
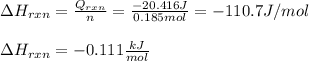
Best regards!