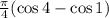Answer:
The result of the integral is
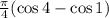
Explanation:
Polar coordinates:
In polar coordinates, we have that:
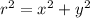
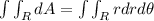
In which r is related to the radius values, while
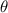 is related to the angles in the trigonometric circle.
is related to the angles in the trigonometric circle.
In this question:
R is the region in the first quadrant
In the first quadrant in the trigonometric circles, the angles go from 0 to
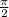 , which means that this are the outer limits of integration.
, which means that this are the outer limits of integration.
Between the circles with center the origin and radii 1 and 2
This means that the inner limits of integration are between 1 and 2.
The integral will be given by:
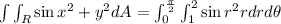
Inner integral:
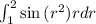
By substituion,
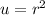
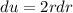
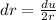
So
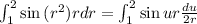 = \frac{1}{2} \int_{1}^{2} \sin{u} du[/tex]
= \frac{1}{2} \int_{1}^{2} \sin{u} du[/tex]
Integral of sine is minus cosine. So
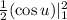
Before replacing, we substitute back u.
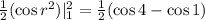
Outer integral:
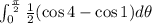
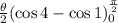
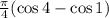
The result of the integral is