Answer: 40% discount
Explanation:
First lets find the difference between original price and sale price so $125-$75= $50
So we get a discount of 50 dollars off the original price
Next lets find out how much of %$125 is that $50 so
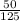 as a decimal is .4 or 40%. To check our work lets multiply 125 by 0.4 so 125*0.4= 50 which is the discount.
as a decimal is .4 or 40%. To check our work lets multiply 125 by 0.4 so 125*0.4= 50 which is the discount.