Answer:
a)
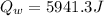
b)
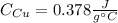
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, when a hot substance is mixed with a cold one, we can evidence how the hot one is able to heat up the cold one as it cools down. Thus, the net heat flow for this problem can be set up as shown below:
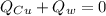
Whereas the heats can be written in terms of mass, specific heat and temperatures:
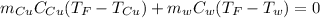
Thus, we proceed as follows:
a. Here we compute Qw:
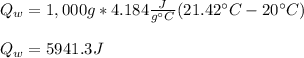
b. Now, since this heat is equal to the negative of the heat contribution of copper (as it cools down), we can compute the specific heat of copper as shown down below:
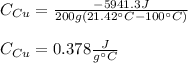
Best regards!