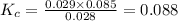Answer: The value of the equilibrium constant Kc for this reaction is 0.088
Explanation:
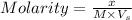
where,
x = given mass
M = molar mass
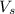 = volume of solution in L
= volume of solution in L
Equilibrium concentration of
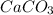 =
=
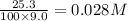
Equilibrium concentration of
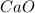 =
=
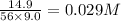
Equilibrium concentration of
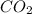 =
=
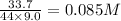
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
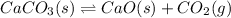
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([CaO]* [CO_2])/([CaCO_3])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/q77m9x5qf7u7k31ln1tlzqkouwfizkrnit.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :