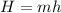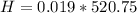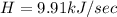Complete Question
Nitrogen (N2) flows through a pipe, entering at at 4 m/sec at 1000 kPa, 2270C. For a pipe inside diameter of 3 cm, find the volumetric flow rate (m3/sec) and the mass flow rate of the gas (kg/sec) assuming you have an ideal gas Then using your ideal gas mass flow rate find the rate at which enthalpy enters the pipe (kJ/sec) NO Cp, Cv, k permitted
Answer:
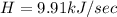
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Velocity
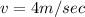
Pressure
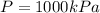
Temperature
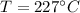
Diameter
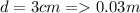
Generally the equation for volumetric Flow Rate is mathematically given by
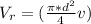
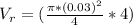
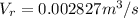
Generally the equation for mass Flow Rate is mathematically given by
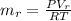
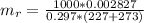
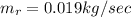
Generally the equation for mass Flow Rate is mathematically given by
Using gas Table for enthalpy Value
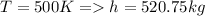
Therefore