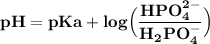Answer:
D H2PO4– + HPO42–
Step-by-step explanation:
The acid dissociation constant for
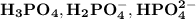 are
are
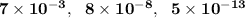 respectively.
respectively.
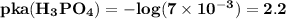
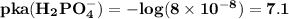
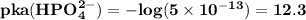
The reason while option D is the best answer is that, the value of pKa for both
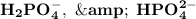 lies on either side of the desired pH of the buffer. This implies that one is slightly over and the other is slightly under.
lies on either side of the desired pH of the buffer. This implies that one is slightly over and the other is slightly under.
Using Henderson-Hasselbach equation: