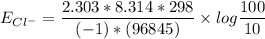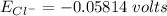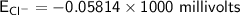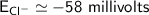Answer:
a. -58 millivolts
Step-by-step explanation:
The given Nernst equation is:
![E_(ion) = 58 millivolts /z \Big[ log_(10) \Big( ([ion]_(out))/([ion]_(in))\Big) \Big]}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/qb4mtb8cqr2og8qsw6h5pe.png)
The equilibrium potential given by the Nernst equation can be determined by using the formula:
![E_(Cl^-) = (2.303*R*T)/(ZF) * log \frac{[Cl^-]_(out)} {[Cl^-]_(in)}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/mainq00w6kniulescuapk3.png)
where:
gas constant(R) = 8.314 J/K/mol
Temperature (T) = (20+273)K
= 298K
Faraday constant F = 96485 C/mol
Number of electron on Cl = -1