Answer:
The total distance is 0.176 m.
Step-by-step explanation:
For t = 0 s to t = 20 ms
initial velocity, u = 0
acceleration, a = 220 m/s^2
time, t = 20 ms
Let the final speed is v.
Use first equation of motion
v = u + at
v = 0 + 220 x 0.02 = 4.4 m/s
Let the distance is s.
Use second equation of motion
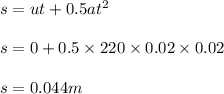
Now the distance is
s' = v x t
s' = 4.4 x 0.03 = 0.132 m
The total distance is
S = s + s' = 0.044 + 0.132 = 0.176 m