Answer:
ρ= 1.378 10⁴ Ω / m
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's use ohm's law
V = i R
R = V / i
let's calculate
R = 9.0 / 230 10⁻⁶
R = 3.9 10⁴ Ω
now we can use the definite of resistance
R = ρ
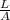
the area of a circle is
A = π r² = π (d/2)²
ρ = R A / L
ρ = π R
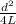
let's calculate
ρ = π 3.9 10⁴
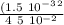
ρ= 1.378 10⁴ Ω / m