Answer:
See Explanation and attachments
Explanation:
Given
See question for data
Solving (a):
The scale used is an ordinal scale.
Ordinals scale uses hierarchy arrangement and the data can be arranged as:
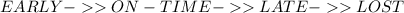
The variable of the delivery performance is qualitative because it is non-numerical
Solving (b): Frequency table
From the table, we have:
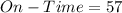
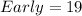
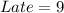
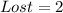
So, the frequency distribution table is:

Solving (c): Frequency table.
To do this, we add another column (Relative Frequency) to the above table.
The relative frequency is calculated as:
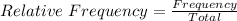
So, we have:
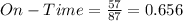
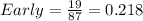
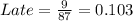
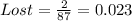
So, the frequency distribution table is:

Solving (d & e): See attachment 1 for bar chart & attachment 2 for pie chart
Solving (f):
From the question, we understand that the object is to return 99% early or on time and never to lose a package.
The analysis is as follows:
Early and On-Time (ET) packages
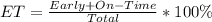
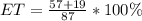
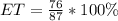
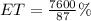
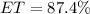
Lost packages
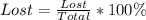
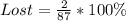
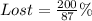
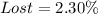
From the above analysis, we can see that 87.4% of the packages were delivered early enough and 2.30% were lost.
The fraction of packages delivered early can be improved and the fraction of lost packages can be reduced by exploring the chances of taking alternative routes when possible.