Step-by-step explanation:
The volume of the gas occupied can be calculated by using the ideal gas equation:
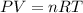
where,
P=pressure of the gas in atm
V=volume of the gas in L.
n=number of moles of the gas
R=0.0821L.atm.mol-1.K-1
T=absolute temperature
To get the volume of the gas, follow the below steps:
1) Calculate the number of moles of gas:
Number of moles of butane=mass of butane given/its molecular mass
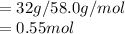
2) Convert temperature into kelvin scale:
T=(45+273)K=318K
3)Convert pressure into atm:
760 mm Hg =1 atm
then,
728 mm Hg=
728 mm Hg x 1 atm /760 mm Hg
=0.957 atm
Substitute all these values in the ideal gas equation to get the volume:
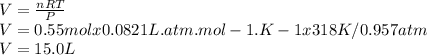
Answer:
The volume of butane gas is 15.0 L