Answer:
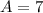
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Pre-Calculus
- Parametric to Rectangular Form Conversion
Calculus
Integrals - Area under the curve
Area of a Curve Formula:
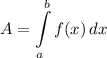
Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
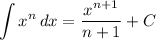
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
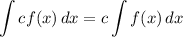
Integration Rule [Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1]:
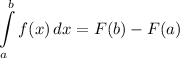
Explanation:
*Note:
The area under the curve is essentially the definition of an integral.
Step 1: Define
Parametric
x = t
y = 3t²
1 ≤ t ≤ 2
Step 2: Rewrite
Rewrite parametric to rectangular form and change bounds of integration.
- [Parametric] Substitute in t: y = 3x²
- [Parametric] Plug in values of t [Bounds]: 1 ≤ x ≤ 2
Step 3: Find Area
Integration.
- Substitute in variables/function [Area]:
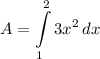
- [Area] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
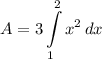
- [Area] Integrate [Integration Rule - Reverse Power Rule]:
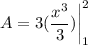
- [Area] Evaluate [Integration Rule - Fundamental Theory of Calculus 1]:
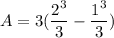
- [Area] (Parenthesis) [Fraction] Evaluate exponents:
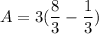
- [Area] (Parenthesis) Subtract:
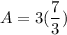
- [Area] Multiply:
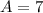
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC
Unit: Area under the curve
Book: College Calculus 10e