Answer:
1) The student's weight on Earth is approximately 687.398 N
2) The student's weight on Mercury is approximately 257.85 N
3) The student's weight on the Sun is approximately 19,164.428 N
Step-by-step explanation:
The mass of the student, m = 70 kg
1) The mass of the Earth, M = 5.972 × 10²⁴ kg
The radius of the Earth, R = 6,371 km = 6.371 × 10⁶ m
The universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67430 × 10⁻¹¹ N·m²/kg²
Mathematically, the universal gravitational law is given as follows;
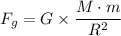
Therefore, we have;
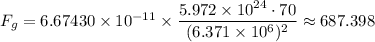
 = W ≈ 687.398 N
= W ≈ 687.398 N
The student's weight on Earth, W ≈ 687.398 N
2) On Mercury, we have;
The mass of Mercury, M₂ = 3.285 × 10²³ kg
The radius of Mercury, R₂ = 2,439.7 km = 2.4397 × 10⁶ m
The universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67430 × 10⁻¹¹ N·m²/kg²
The universal gravitational law is
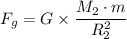
Therefore, we have;
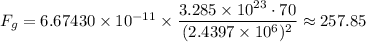
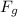 = W₂ ≈ 257.85 N
= W₂ ≈ 257.85 N
The student's weight on Mercury, W₂ ≈ 257.85 N
3) On the Sun, we have;
The mass of the Sun, M₃ ≈ 1.989 × 10³⁰ kg
The radius of the Sun, R₃ ≈ 696,340 km = 6.9634 × 10⁸ m
The universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67430 × 10⁻¹¹ N·m²/kg²
The universal gravitational law is
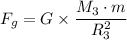
Therefore, we have;
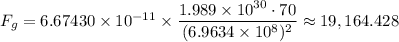
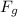 = W₃ ≈ 19,164.428 N
= W₃ ≈ 19,164.428 N
The student's weight on the Sun, W₃ ≈ 19,164.428 N