Answer:
The new volume of the gas when the pressure is changed to 2.84 atm is 822.82 mL.
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law says that "The volume occupied by a given gaseous mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to pressure." That is, if the pressure increases, the volume decreases, while if the pressure decreases, the volume increases.
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
or
P * V = k
Assuming that you have a certain volume of gas V1 that is at a pressure P1 at the beginning of the experiment, by varying the volume of gas to a new value V2, then the pressure will change to P2, and it will be fulfilled:
P1*V1= P2*V2
In this case:
- P1= 9.86 atm
- V1= 237 mL
- P2= 2.84 atm
- V2=?
Replacing:
9.86 atm* 237 mL= 2.84 atm*V2
and solving you get:
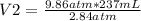
V2= 822.82 mL
The new volume of the gas when the pressure is changed to 2.84 atm is 822.82 mL.