Answer:
3. There is enough information to prove that ΔABC and ΔDEF are congruent using the Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) congruency theorem
4. More information is required to prove that ΔGFH and ΔJKL are congruent
5. ∠B ≅ ∠Y
6. ∠A ≅ ∠X
Explanation:
3. In triangle ΔABC, and triangle ΔDEF, we have;
Corresponding angles ∠A and ∠D are congruent
Corresponding angles ∠C and ∠F are congruent
Corresponding side in between the given angles
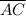 and
and
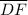 are congruent
are congruent
Therefore ΔABC is congruent to ΔDEF by the Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) rule of congruency
4. The corresponding angles ∠F and ∠J in triangle ΔGFH and triangle ΔJKL are congruent as well as the corresponding adjacent sides to the given angles and the corresponding opposite sides to the given angles are congruent, however, there is not enough information to prove that the two triangles are congruent
The included angles, ∠H and ∠L between the sides congruent corresponding sides should be congruent or the other adjacent sides
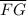 and
and
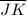 to the congruent angles ∠F and ∠J should be congruent for the triangles ΔGFH and ΔJKL to be congruent
to the congruent angles ∠F and ∠J should be congruent for the triangles ΔGFH and ΔJKL to be congruent
5. Given
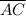 ≅
≅
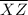 , ∠C ≅ ∠Z, using the Angle-Angle-Side, AAS, rule of congruency, we have;
, ∠C ≅ ∠Z, using the Angle-Angle-Side, AAS, rule of congruency, we have;
The angles adjacent to ∠C and ∠Z, and opposite to
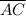 and
and
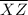 , which are B and ∠Y are congruent
, which are B and ∠Y are congruent
Therefore, we have;
∠B ≅ ∠Y using AAS rule of congruency
6. Using Angle-Side-Angle, ASA, rule, given;
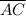 ≅
≅
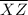 , ∠C ≅ ∠Z, then the angles on the other side of
, ∠C ≅ ∠Z, then the angles on the other side of
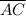 and
and
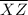 which are ∠A and ∠X should be congruent, we have;
which are ∠A and ∠X should be congruent, we have;
∠A ≅ ∠X