Answer:
A) the initial point all energy is elastic potential and the final point all energy is kinetic
B) a bar graph the two bars have the same height and the sum of their height is the initial energy
C) two bars, one for the kinetic energy and the other for the gravitational potential energy.
Step-by-step explanation:
A) For this exercise we must use the energy conservation relations
starting point. When the spring is compressed
Em₀ = K_e = ½ k x²
end point, at the bottom of the loop
Em_f = K = ½ m v²
energy is conserved
Em₀ = Em_f
½ k x² = ½ m v²
v =
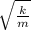 x
x
In a bar graph the initial point all energy is elastic potential and the final point all energy is kinetic
B) intermediate point in a quarter of the radius
In this case we use the lower part of the loop as the starting point and the quarter part of the bow as the end point.
Em₀ = K
Em_f = K + U = ½ m v² + m g R
in a bar graph the two bars have the same height and the sum of their height is the initial energy
C) End point highest part of the loop
starting point, bottom of loop
Emo = K = ½ m v₀²
from part A of the exercise we saw that it is equal to the elastic energy of the spring
final point. Highest part of the loop
Emf = K + U
Em_f = ½ m
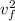 + mg (2R)
+ mg (2R)
where R is the radius of the loop
Em₀ = Em_f
1/2 m v₀² = 1/2 m v_{f}^2+ mg 2R
v₀² = v_f^2 + 4gR
In a bar graph there are two bars, one for the kinetic energy and the other for the gravitational potential energy. The sum of the heights of these bars is the initial energy, so the energy is transformed but not created or destroyed in the process.