Answer:
The inverse of g(x) is
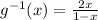
The domain of g(x) is (-∞,-2)U(-2,∞)
The domain of f(x) is (-∞,-1)U(-1,1)U(1,∞)
Explanation:
Find the inverse of g(x).
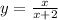
Solve for x
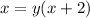
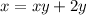
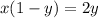
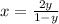
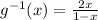
Find the domain of g(x)
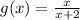
Numerator and denominator have domain
(-∞,∞).
However, g(x) is undefined if the denominator is 0. Hence, x=-2 must be taken out of the domain. So, the domain of g(x) is
(-∞,-2)U(-2,∞).
Find the domain of f(x)
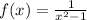
The numerator and denominator have the domain
(-∞,∞)
However, f(x) is undefined if the denominator is 0. This rules out +1 and -1. So, the domain of f(x) is
(-∞,-1)U(-1,1)U(1,∞)
I am not sure what you mean for (ii).