Answer:
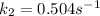
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information, it turns out possible for us to calculate the rate constant at 55 °C by using the temperature-variable version of the Arrhenius equation:
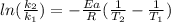
Thus, we plug in the temperatures, activation energy and universal constant of gases in consistent units to obtain:
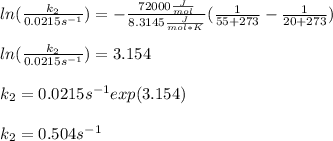
Regards!