Answer:
V = mRT / (
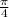 d²)PM
d²)PM
Therefore, pressure decreases as velocity increases.
This is a hypothetical concept as the friction which causes the velocity to increases also makes the pressure decrease.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the data in the question;
we know that an ideal gas equation is;
 = PM/RT --------------- let this be equation 1
= PM/RT --------------- let this be equation 1
P is pressure, M is molecular weight, R is universal gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
The volumetric flow rate from the continuity equation is;
Q = AV
and A =
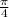 d²
d²
so, Q = (
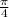 d²)V ---------let this be equation 2
d²)V ---------let this be equation 2
Expression for mass m in flowrate is;
m = Q
 ------------------let this be equation 3
------------------let this be equation 3
so, m = (
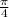 d²)V × PM/RT
d²)V × PM/RT
solve for V
V = mRT / (
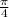 d²)PM
d²)PM
Therefore, pressure decreases as velocity increases.
This is a hypothetical concept as the friction which causes the velocity to increases also makes the pressure decrease.